Configuring DNS for a Domain
The Domain Name![]() A domain name is an identification string that defines a realm of administrative autonomy, authority, or control on the Internet. Domain names are formed by the rules and procedures of the Domain Name System (DNS). System (DNS
A domain name is an identification string that defines a realm of administrative autonomy, authority, or control on the Internet. Domain names are formed by the rules and procedures of the Domain Name System (DNS). System (DNS![]() The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical distributed naming system for computers, services, or any resource connected to the Internet or a private network. It associates various information with domain names assigned to each of the participating entities. A Domain Name Service resolves queries for these names into IP addresses for the purpose of locating computer services and devices worldwide. By providing a worldwide, distributed keyword-based redirection service, the Domain Name System is an essential component of the functionality of the Internet.) is a hierarchical naming system that translates understandable domain names into the numerical identifiers (IP addresses) associated with web hosts. Such translation is called resolving. When you add a domain name (using Websites & Domains > Add New Domain), you should choose the role of Panel in resolving your resources: It can directly process all translation requests, be a backup server, or pass the translation requests to a remote server. This role can be changed for existing domain names (Websites & Domains > click a domain name> DNS Settings). We discuss details about each of the roles and provide instructions how to assign them next in this section.
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical distributed naming system for computers, services, or any resource connected to the Internet or a private network. It associates various information with domain names assigned to each of the participating entities. A Domain Name Service resolves queries for these names into IP addresses for the purpose of locating computer services and devices worldwide. By providing a worldwide, distributed keyword-based redirection service, the Domain Name System is an essential component of the functionality of the Internet.) is a hierarchical naming system that translates understandable domain names into the numerical identifiers (IP addresses) associated with web hosts. Such translation is called resolving. When you add a domain name (using Websites & Domains > Add New Domain), you should choose the role of Panel in resolving your resources: It can directly process all translation requests, be a backup server, or pass the translation requests to a remote server. This role can be changed for existing domain names (Websites & Domains > click a domain name> DNS Settings). We discuss details about each of the roles and provide instructions how to assign them next in this section.
DNS Name Resolving
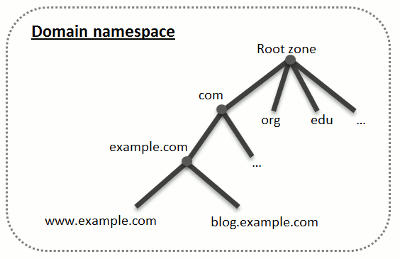
DNS is based on a hierarchical tree structure called the domain namespace. This global namespace contains all possible domain names and is divided into logical parts - domain zones (see the picture below). A domain zone is a part of the namespace that contains the addresses of particular domains. Addresses are stored in a file on a separate name server![]() In computing, a name server is a computer server that hosts a network service for providing responses to queries against a directory service. It maps a human-recognizable identifier to a system-internal, often numeric, identification or addressing component. This service is performed by the server according to a network service protocol. with authority for that zone. For example, when a browser tries to access www.example.com, it gets the site's IP address
In computing, a name server is a computer server that hosts a network service for providing responses to queries against a directory service. It maps a human-recognizable identifier to a system-internal, often numeric, identification or addressing component. This service is performed by the server according to a network service protocol. with authority for that zone. For example, when a browser tries to access www.example.com, it gets the site's IP address![]() An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label assigned to each device (e.g., computer, printer) participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two principal functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing from a server with authority for the example.com zone. For more information about how DNS works, refer to the respective documentation. You can find it in numerous sources on the Internet, for example, Microsoft TechNet.
An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label assigned to each device (e.g., computer, printer) participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two principal functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing from a server with authority for the example.com zone. For more information about how DNS works, refer to the respective documentation. You can find it in numerous sources on the Internet, for example, Microsoft TechNet.
When you purchase a domain, a registrar gives you access to the settings for the DNS zone responsible for your domain and its subdomains. You can either allow the registrar to manage the zone, or delegate the zone to Panel. The latter option gives you the ability to manage a zone directly from your customer account. For information about how to delegate your zone to the Panel, refer to the section Panel as a Master DNS Server.
If you are an advanced user and already have a DNS server that you want to give authority for your zone, you can set up Panel to be a slave (also called secondary) DNS server. In this case, Panel just stores a copy of your zone and you do not have the option to manage it from the Hosting Control Panel. The Panel DNS server will be used only if your primary name server becomes inaccessible or inoperable. For information about how to make Panel act as a secondary DNS server, refer to the section Panel as a Slave DNS Server.
If you decide not to use Panel as a DNS server, but would rather utilize a 3rd party's name servers, please see how to switch off the Panel's DNS server and manage your zone remotely, in the section: 3rd Party DNS Servers.