Installing a SSL Certificate
After you purchase and receive your issued SSL![]() Transport Layer Security (TLS) and its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), are cryptographic protocols that provide communication security over the Internet.[1] TLS and SSL encrypt the segments of network connections at the Application Layer for the Transport Layer, using asymmetric cryptography for key exchange, symmetric encryption for confidentiality, and message authentication codes for message integrity. certificate, secure your website with the following steps.
Transport Layer Security (TLS) and its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), are cryptographic protocols that provide communication security over the Internet.[1] TLS and SSL encrypt the segments of network connections at the Application Layer for the Transport Layer, using asymmetric cryptography for key exchange, symmetric encryption for confidentiality, and message authentication codes for message integrity. certificate, secure your website with the following steps.
To secure a website with an SSL certificate:
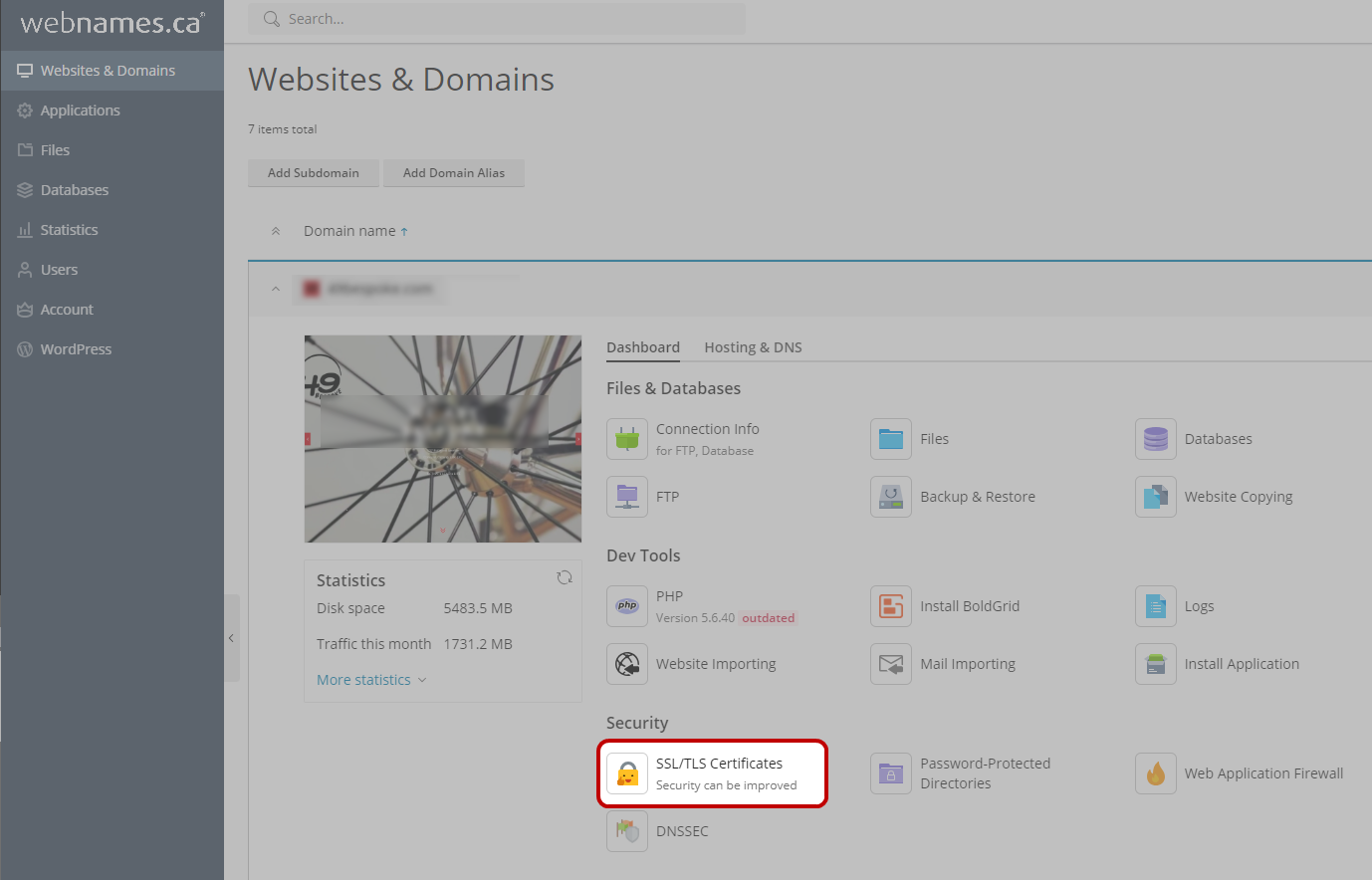
- Go to the SSL certificates repository via Websites & Domains, click SSL/TLS
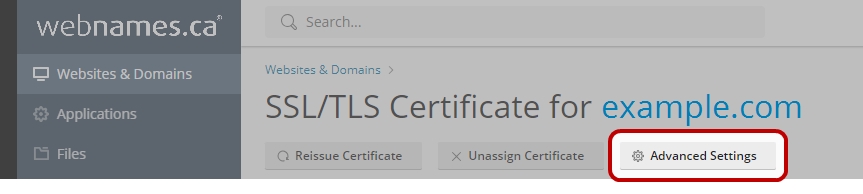
 The Transport Layer Security protocol aims primarily to provide privacy and data integrity between two communicating computer applications.[1]:3 When secured by TLS, connections between a client (e.g., a web browser or email program) and a server (website or email server) are private (or secure), authenticated, and unaltered. Certificates and then click the Advanced Settings button.
The Transport Layer Security protocol aims primarily to provide privacy and data integrity between two communicating computer applications.[1]:3 When secured by TLS, connections between a client (e.g., a web browser or email program) and a server (website or email server) are private (or secure), authenticated, and unaltered. Certificates and then click the Advanced Settings button.
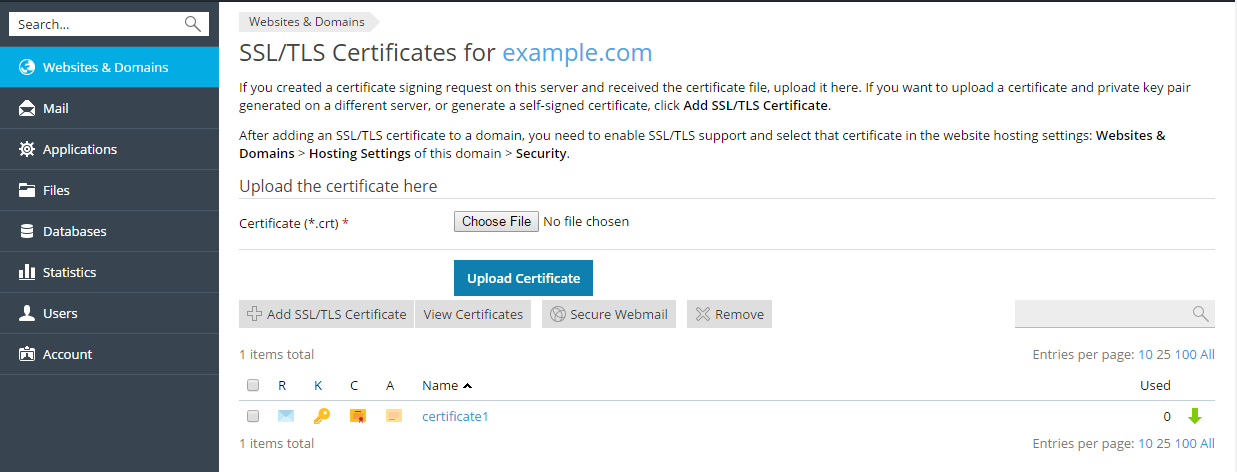
- Upload the SSL certificate: Click Choose file in the middle of the screen and navigate to the location on your computer where you have saved your issued certificate. Select it, and then click Upload Certificate.This will upload and install the certificate against the corresponding private key.
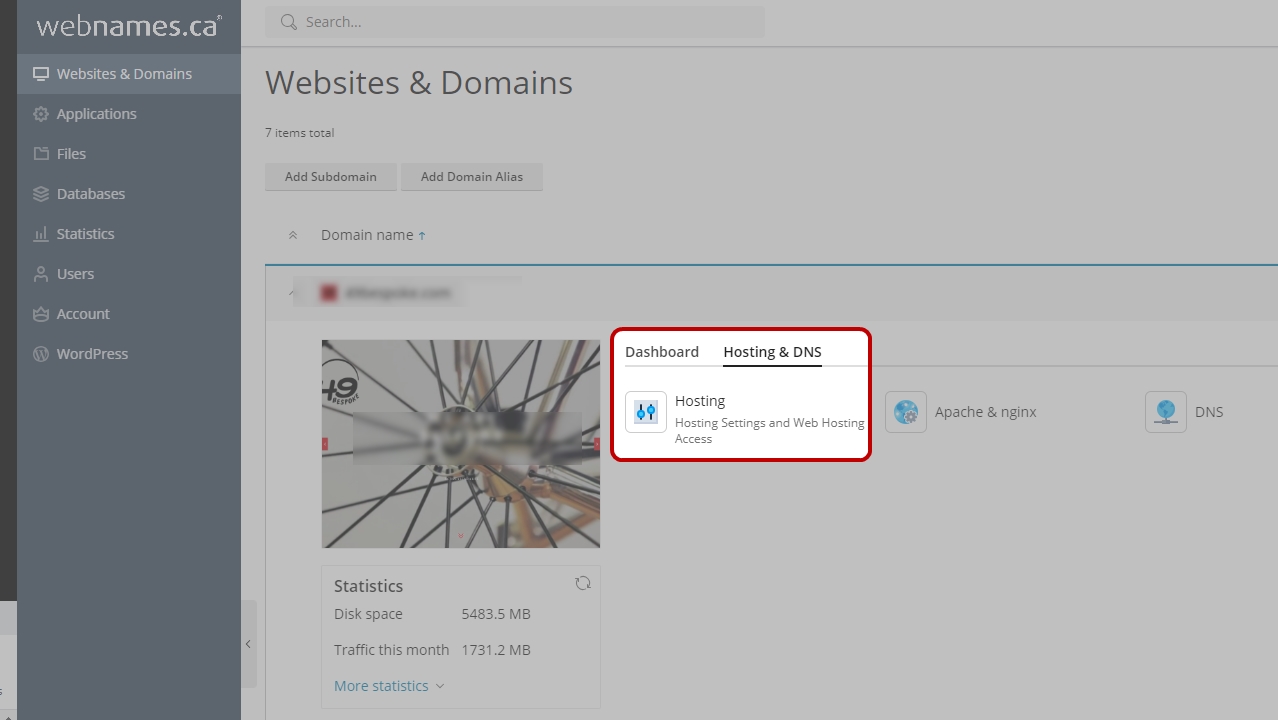
- Next, to assign the uploaded certificate to your website, return to the Websites & Domains tab, and click Hosting Settings link under the name of the website you wish to secure.
- To switch on SSL protection, under SSL/TLS support, ensure the Enable box is checked.
- From the SSL certificate menu, select the SSL certificate you uploaded in step 2 and click Save.